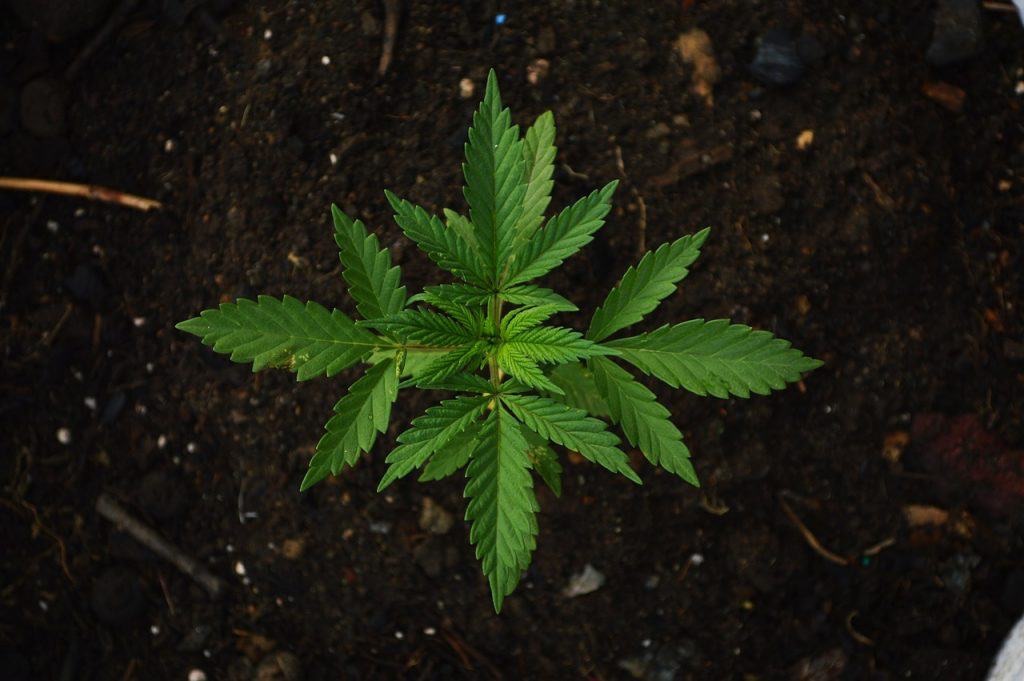
Introduction
Understanding the anatomy of the cannabis plant is crucial for both growers and consumers. From the tiny seed that sparks the journey to the mature plant ready for harvest, each part plays a vital role in the plant’s development and the quality of its final product. This guide will walk you through the key parts of the cannabis plant and their functions, from the initial seed to the fully grown and harvested plant.
1. The Seed: The Starting Point
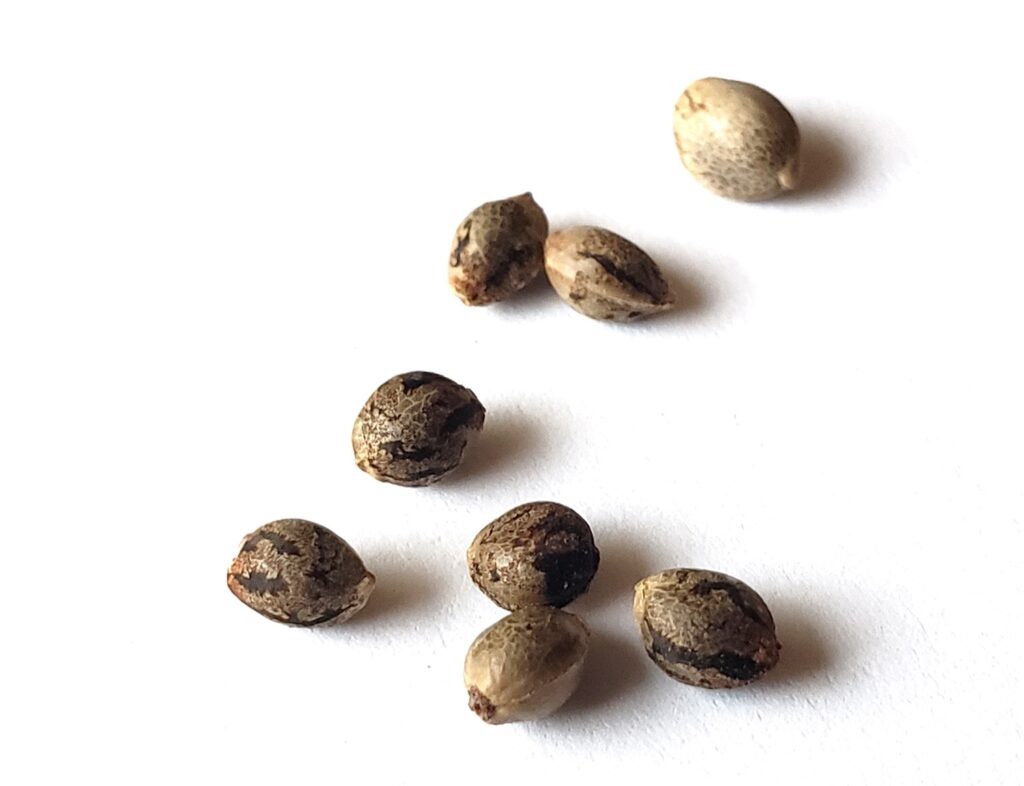

The journey of every cannabis plant begins with a seed. Cannabis seeds are small, hard-shelled, and vary in color from light to dark brown. The quality of the seed can determine the health and yield of the plant.
Germination
Germination is the process where the seed sprouts and the first root, known as the radicle, emerges. This stage is critical as it sets the foundation for the plant’s growth. Conditions like moisture, warmth, and darkness are essential for successful germination.
2. The Seedling: Early Growth
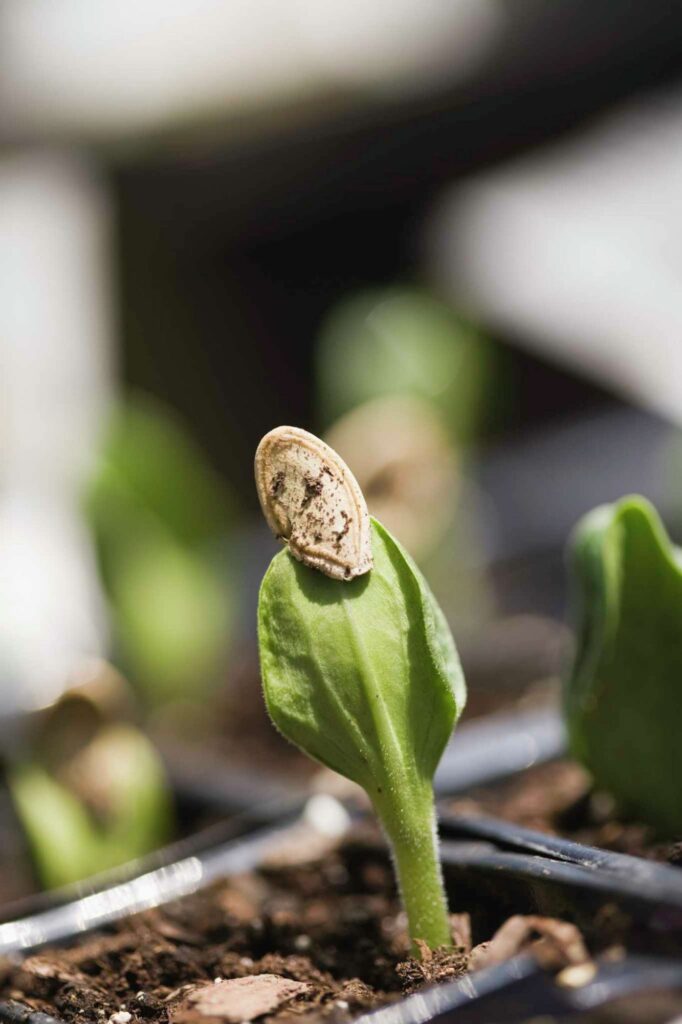

Once the seed has germinated, it enters the seedling stage. During this phase, the plant develops its first leaves, known as cotyledons, which are small and rounded. These leaves help the plant to begin photosynthesis, the process by which it converts light into energy.
True Leaves

After the cotyledons, the plant will develop its first set of true leaves. These leaves are recognizable by their serrated edges, a characteristic of cannabis. The seedling stage is delicate, and the plant requires a carefully controlled environment with plenty of light, proper humidity, and nutrients.
3. The Vegetative Stage: Rapid Growth
The vegetative stage is when the cannabis plant begins to grow rapidly. During this phase, the plant focuses on developing a strong root system, thicker stems, and large fan leaves that are essential for photosynthesis.
Parts Developed During Vegetative Stage:
- Roots: The root system is crucial for the plant’s ability to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. A healthy root system supports robust growth and development.
- Stems: The stem becomes thicker and taller during the vegetative stage, providing structural support for the plant. The stem also transports nutrients and water from the roots to other parts of the plant.
- Fan Leaves: These large, broad leaves are essential for capturing sunlight and driving the process of photosynthesis. Fan leaves are the primary energy source for the plant during its growth stages.
4. The Pre-Flowering Stage: Signs of Maturity
As the cannabis plant approaches maturity, it enters the pre-flowering stage. During this phase, the plant begins to show its sex—whether it’s male or female.
Identifying Male and Female Plants
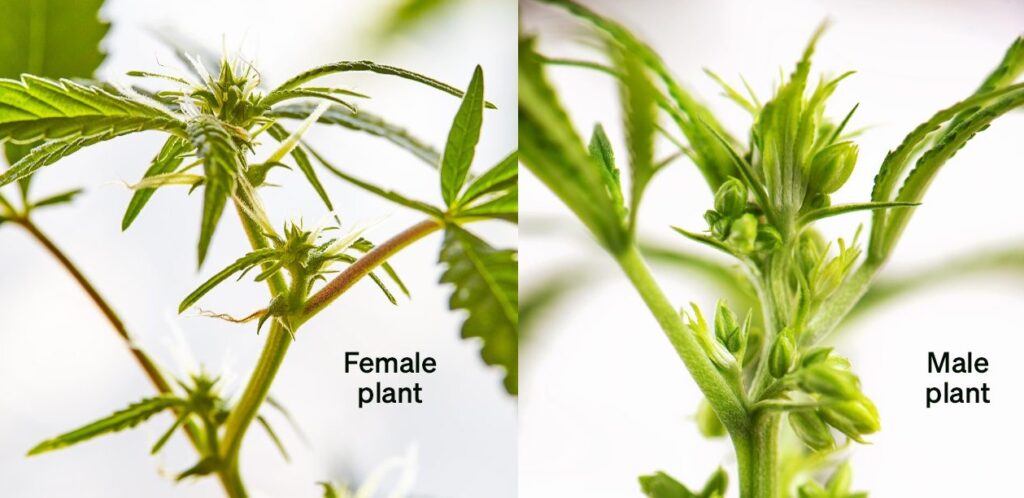

- Male Plants: Male plants develop pollen sacs, which are small, round growths that appear at the nodes (the points where the leaves and branches meet the stem). Male plants are typically removed by growers to prevent them from pollinating female plants.
- Female Plants: Female plants develop pistils, which are hair-like structures that emerge from the calyxes (small, tear-shaped nodes). These pistils are the first signs that the plant will produce flowers (buds).
5. The Flowering Stage: Bud Development
The flowering stage is the most critical phase for cannabis growers, as it’s when the plant produces buds—the part of the plant that is harvested and consumed.
Parts Developed During Flowering Stage:

- Calyxes: Calyxes are small, tear-shaped nodes that form the base of the flower. They contain the ovary and are covered in trichomes, which produce cannabinoids like THC and CBD.
- Pistils: The pistils are the hair-like structures that emerge from the calyxes. They initially appear white but change color (to orange, red, or brown) as the plant matures.
- Sugar Leaves: Sugar leaves are small leaves that grow within the buds. They are covered in trichomes and are often trimmed during the harvesting process, though they can be used to make concentrates.
- Trichomes: As discussed earlier, trichomes are glandular structures that produce and store cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids. They appear as tiny, crystal-like structures on the surface of the buds, giving them a frosty appearance.
6. The Harvest: Bringing It All Together
Once the cannabis plant has fully matured and the trichomes have reached their desired level of potency, it’s time to harvest.
Harvesting Process:
- Cutting: The plant is cut down, and the branches are separated for drying.
- Drying and Curing: The branches are hung upside down in a controlled environment to dry. After drying, the buds are trimmed and placed in airtight containers to cure, which enhances their flavor and potency.
- Final Product: The final product is the harvested buds, which are rich in cannabinoids and terpenes, ready for consumption in various forms, such as smoking, vaping, or edibles.
Conclusion
The journey of the cannabis plant from seed to harvest is a fascinating process, with each stage playing a crucial role in the plant’s development and the quality of the final product. Understanding the anatomy of the cannabis plant helps both growers and consumers appreciate the complexity and care that goes into producing high-quality cannabis. Whether you’re growing your own or enjoying the final product, knowing these key stages and parts of the plant can deepen your appreciation for this incredible plant.