Introduction
The terms cannabis and hemp are often used interchangeably, but they refer to distinct varieties of the Cannabis sativa plant. While both cannabis and hemp belong to the same plant species, they have different uses, chemical compositions, and legal statuses. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone interested in the cannabis industry, whether for recreational, medicinal, or industrial purposes.
What is Cannabis?
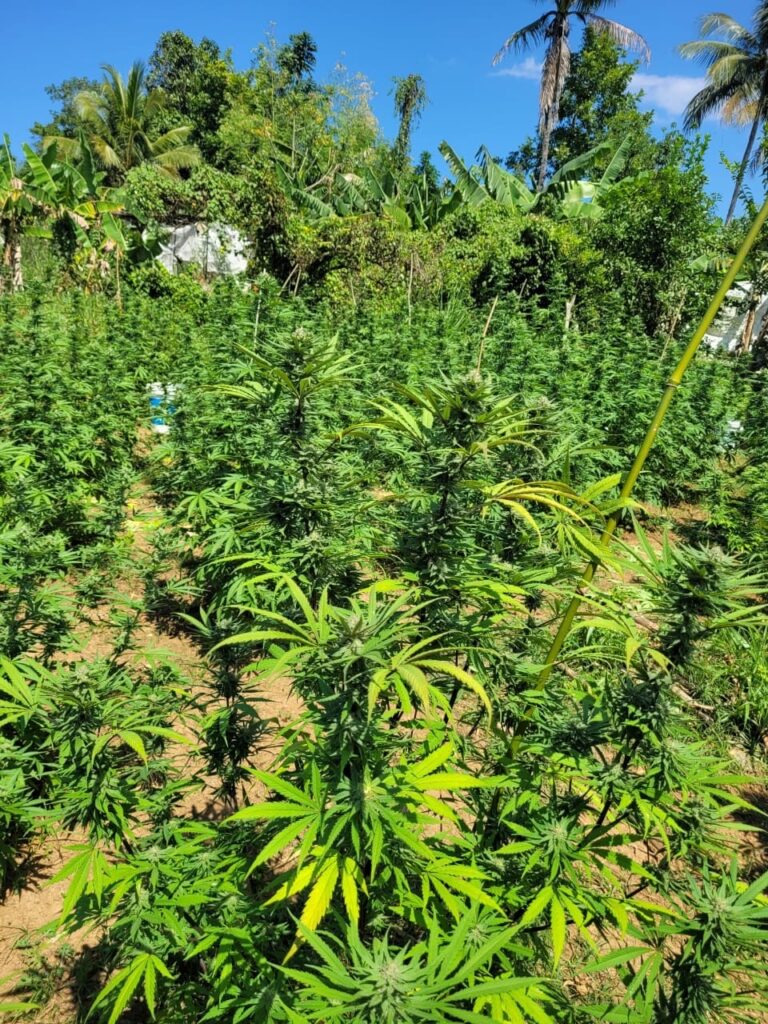

Cannabis is a term that broadly refers to a group of plants in the Cannabis sativa genus that are cultivated for their psychoactive properties. These plants are rich in THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the compound responsible for the “high” associated with marijuana use. Cannabis is primarily grown for its flowers, which contain high concentrations of cannabinoids, particularly THC and CBD (cannabidiol).
Characteristics of Cannabis
- THC Content: Cannabis plants typically contain THC levels ranging from 5% to 30%, making them potent enough to produce psychoactive effects.
- Cultivation Purpose: Cannabis is primarily grown for recreational and medicinal purposes, focusing on producing flowers that are rich in THC and other cannabinoids.
- Legal Status: The legal status of cannabis varies widely by country and region. In some places, it is legal for both medicinal and recreational use, while in others, it remains strictly prohibited.
What is Hemp?
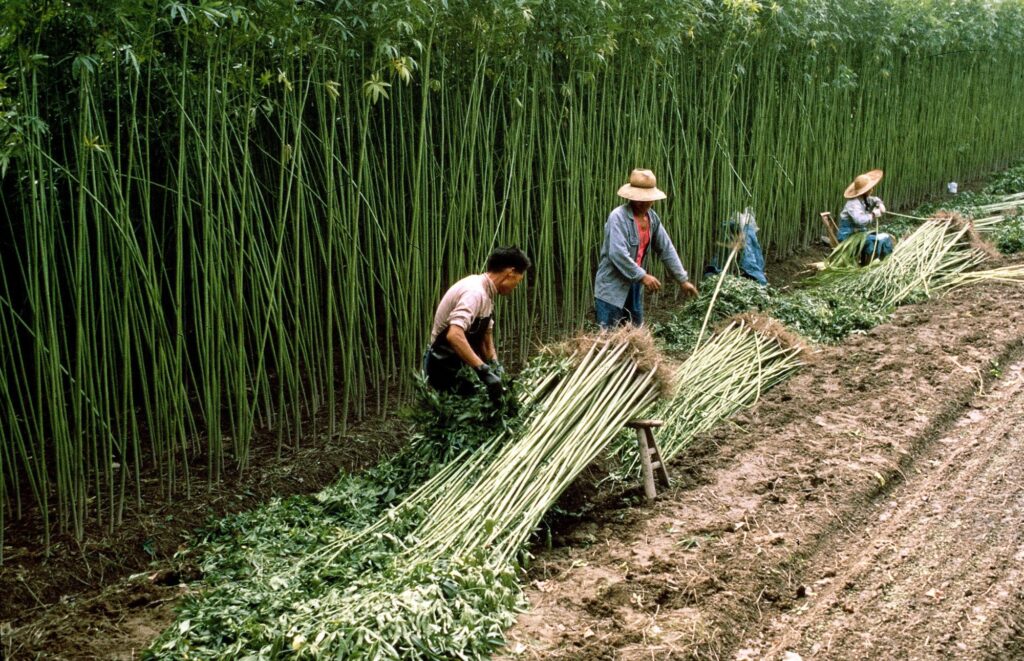

Hemp refers to cannabis plants that are cultivated for industrial purposes rather than for their psychoactive effects. Hemp plants have a very low THC content, typically less than 0.3%, which is not enough to produce any intoxicating effects. Instead, hemp is valued for its strong fibers, seeds, and oil, which are used in a wide range of products from textiles to food supplements.
Characteristics of Hemp
- THC Content: Hemp contains less than 0.3% THC, which is the legal threshold in many countries, including the United States. This low level of THC ensures that hemp products do not produce psychoactive effects.
- CBD Content: Hemp often has a higher concentration of CBD, a non-psychoactive cannabinoid known for its potential therapeutic benefits.
- Cultivation Purpose: Hemp is grown primarily for industrial uses, including the production of textiles, paper, biofuels, building materials, and health supplements like CBD oil.
- Legal Status: Hemp is legal in many parts of the world, especially where cannabis remains restricted. The 2018 Farm Bill in the United States, for example, legalized the cultivation of hemp and the production of hemp-derived products.
Key Differences Between Cannabis and Hemp
Chemical Composition
- THC Levels: The primary difference between cannabis and hemp is the level of THC. Cannabis is bred to have high THC levels, while hemp is bred to have minimal THC.
- CBD Levels: Hemp typically has higher levels of CBD compared to cannabis, making it the preferred source for CBD extraction.
Legal Status
- Cannabis: Due to its high THC content, cannabis is subject to strict regulations and is illegal in many places. Its legal status is often debated and varies significantly depending on local laws.
- Hemp: Hemp is generally legal in more places due to its low THC content. Products derived from hemp, such as CBD oil, are widely available and legally sold in many countries.
Uses and Applications
- Cannabis: Used primarily for recreational and medicinal purposes. Cannabis products include dried flowers, edibles, concentrates, and tinctures, all of which are intended for consumption to experience the psychoactive effects of THC or the therapeutic benefits of CBD.
- Hemp: Used in a wide range of industrial applications. Hemp fibers are used to make textiles, ropes, and building materials, while hemp seeds are used for nutritional supplements, and hemp oil is used in cosmetics and food products.
Cultivation Practices
- Cannabis: Grown in controlled environments (indoors or in greenhouses) to maximize the production of THC-rich flowers. These plants are typically shorter and bushier.
- Hemp: Grown outdoors in large fields, hemp plants are taller and more fibrous. The focus is on producing strong stalks for fiber and seeds rather than cannabinoid-rich flowers.
Conclusion
While cannabis and hemp both come from the same species, Cannabis sativa, they are cultivated and used for very different purposes. Cannabis is primarily used for its psychoactive properties, thanks to its high THC content, while hemp is valued for its industrial uses and high CBD content. Understanding the differences between these two plants is essential for making informed decisions about their use, whether for recreational, medicinal, or industrial purposes.