Introduction
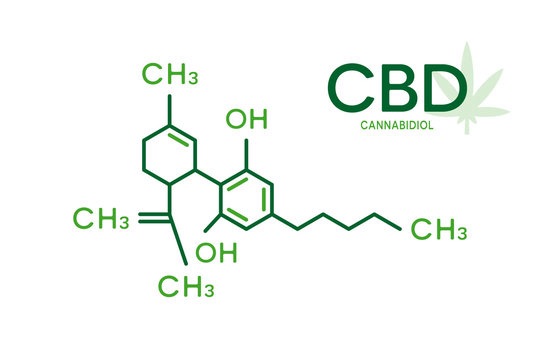
CBD (Cannabidiol) is one of the most well-known and widely researched cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. Unlike THC, CBD is non-psychoactive, meaning it doesn’t produce the “high” typically associated with cannabis use. Instead, CBD is celebrated for its wide range of potential therapeutic benefits, making it a popular choice for those seeking natural remedies without the intoxicating effects.
What is CBD?
CBD is one of over 100 cannabinoids present in cannabis and hemp plants. It interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex cell-signaling system that plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, including pain, mood, sleep, and immune function.
How CBD Works
CBD works by interacting with the ECS, particularly with the CB1 and CB2 receptors. Unlike THC, which binds directly to CB1 receptors in the brain, CBD doesn’t directly activate these receptors. Instead, it influences the body’s natural cannabinoids to enhance their ability to bind to receptors. This indirect interaction allows CBD to modulate various functions in the body without causing a high.
Therapeutic Benefits of CBD
CBD has been the focus of numerous studies due to its potential to treat a wide range of conditions. Its non-psychoactive nature makes it an appealing option for those looking to experience the therapeutic benefits of cannabis without the mind-altering effects.
Key Benefits
- Pain Relief: CBD is widely recognized for its analgesic properties. It can help manage chronic pain conditions, including arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and neuropathic pain.
- Anxiety and Depression: CBD has shown promise in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression, offering a natural alternative to pharmaceutical medications.
- Anti-inflammatory: CBD’s anti-inflammatory properties make it useful in treating conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, acne, and other inflammation-related disorders.
Additional Benefits
- Epilepsy: CBD has been extensively studied for its effectiveness in treating epilepsy, particularly in reducing the frequency and severity of seizures in conditions like Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
- Sleep Disorders: CBD may help improve sleep quality by addressing the root causes of insomnia, such as anxiety or pain.
- Neuroprotection: Emerging research suggests that CBD has neuroprotective properties, potentially offering benefits for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s disease.
Potential Side Effects
While CBD is generally well-tolerated, some people may experience side effects, especially when taken in high doses.
Common Side Effects
- Dry Mouth: CBD can decrease saliva production, leading to dry mouth.
- Drowsiness: High doses of CBD may cause drowsiness, making it important to consider the timing of your dose.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Some users may experience nausea, diarrhea, or changes in appetite.
How to Use CBD
CBD is available in various forms, making it easy to incorporate into your wellness routine. Popular methods of consumption include:
- Oils and Tinctures: These are taken sublingually (under the tongue) for quick absorption into the bloodstream.
- Edibles: CBD-infused gummies, chocolates, and beverages provide a tasty and discreet way to consume CBD.
- Topicals: Creams, balms, and lotions infused with CBD can be applied directly to the skin to target localized pain and inflammation.
- Vapes: CBD vape oils offer fast-acting effects but may not be suitable for everyone due to concerns about lung health.
Conclusion
CBD (Cannabidiol) is a versatile and non-psychoactive cannabinoid that offers a wide range of potential health benefits. Whether you’re looking to manage chronic pain, reduce anxiety, or improve sleep, CBD provides a natural alternative to traditional pharmaceuticals. As research continues to expand our understanding of CBD, its popularity is likely to grow, making it an essential part of the modern wellness landscape.