Introduction
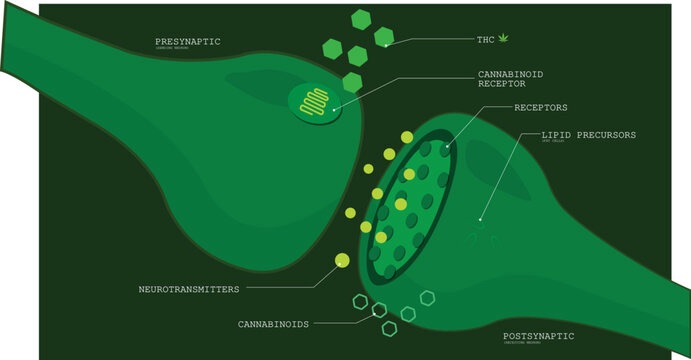
Did you know your body has a special system just for processing cannabinoids, the compounds found in cannabis? It’s called the endocannabinoid system (ECS), and it plays a major role in keeping your body balanced and healthy. This system includes CB1 and CB2 receptors, which are like tiny locks that cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, can open to create various effects. In this blog post, we will explore what the ECS is, how CB1 and CB2 receptors work, and why they are important.
What is the Endocannabinoid System (ECS)?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system that exists in all humans and many animals. It was discovered in the 1990s when scientists were researching THC, the well-known compound in cannabis. The ECS is involved in regulating a variety of important functions in the body, such as:
- Mood
- Sleep
- Appetite
- Memory
- Pain and inflammation
- Immune response
The ECS has three main parts:
- Endocannabinoids: These are natural chemicals made by your body that are similar to cannabinoids found in cannabis. Two of the most studied endocannabinoids are anandamide and 2-AG.
- Receptors (CB1 and CB2): These are special spots on cells where endocannabinoids and cannabinoids (like THC and CBD) can bind, triggering different effects.
- Enzymes: These break down endocannabinoids once they have done their job, ensuring the body maintains balance.
What Are CB1 and CB2 Receptors?
CB1 and CB2 receptors are two main types of receptors in the ECS. They act like gateways that allow cannabinoids and endocannabinoids to send signals to different parts of the body.
CB1 Receptors
- Location: Mainly found in the brain and central nervous system, but also in smaller amounts in other areas, like the liver and lungs.
- Function: CB1 receptors are involved in controlling things like mood, memory, pain, and appetite. When THC binds to CB1 receptors, it produces the “high” or euphoria associated with cannabis.
CB2 Receptors
- Location: Mostly located in the immune system and other parts of the body like the spleen, tonsils, and digestive system.
- Function: CB2 receptors help regulate the body’s response to pain and inflammation. Unlike CB1 receptors, they don’t make you feel “high” when activated, which is why CBD, which primarily affects CB2 receptors, does not have psychoactive effects.
How Do CB1 and CB2 Receptors Work Together?
Both CB1 and CB2 receptors help the body stay in a balanced state, or homeostasis. Here’s how they work:
- CB1 Receptors: When THC binds to CB1 receptors, it can affect how the brain works. This is why THC can change how you feel, think, and experience pain. CB1 receptors also play a role in regulating mood, which can be why cannabis is sometimes used to help with anxiety or depression.
- CB2 Receptors: These receptors mainly help control how the body reacts to pain and inflammation. For example, CBD binds to CB2 receptors and can help reduce inflammation without affecting your brain, making it useful for conditions like arthritis or other inflammatory disorders.
Why is the Endocannabinoid System Important?
The ECS is essential for maintaining balance in the body. When this system is working properly, it helps regulate many important functions, keeping everything in harmony. If the ECS is not working correctly, it can contribute to various health problems like chronic pain, mood disorders, and immune system issues.
By understanding how CB1 and CB2 receptors work, we can see why cannabis can have such a wide range of effects on the body and how it might be used to treat different health conditions.
Conclusion
The endocannabinoid system (ECS), along with its CB1 and CB2 receptors, is a vital part of our bodies that helps regulate many functions to keep us healthy. Knowing how this system works can help us better understand the effects of cannabis and the potential benefits it may offer. As more research is conducted, we’ll continue to learn more about the ECS and how we can use it to improve our health.